The line between data privacy and security often blurs. While both are instrumental in establishing trust and ensuring compliance, understanding their distinct roles and implications is key.
For businesses operating online, a clear grasp of these concepts not only safeguards against potential breaches and repercussions but also improves the trust customers place in them.
In this article I’ll explain the nuances of data privacy vs data security, highlighting global regulations, best practices, and the inherent interplay between them.
- Data privacy and security are distinct but intertwined concepts vital for online trust and compliance.
- Data privacy focuses on ethical use, while data security emphasizes protection from breaches.
- Strong security measures protect data, but ensuring its ethical use is equally important for upholding privacy.
Table of Contents
PRO TIP: Take the hassle of writing your own privacy policy away with our privacy policy generator trusted by over 200,000 businesses. It’ll save you hours of work and possible costly legal mistakes.
What Is Data Privacy?
Data privacy is about safeguarding personal information shared over the internet and is the digital equivalent of someone respecting your personal boundaries and secrets. It focuses on ensuring that this data isn’t misused or accessed without permission.
While security is a part of it, online data privacy goes beyond just technical measures. It dives into the ethics of how data should be treated which is quite important.
For instance, if a customer gives you their email address for a newsletter, it’s not just about keeping that email safe from hackers. It’s also about not sharing it with third parties without clear consent or using it for unrelated purposes.
There’s a significant human element here. When users hand over their data, they’re placing a lot of trust in you. They believe that you’ll handle their information with care, respect their choices, and be transparent about any data practices.
PRO TIP: It’s essential to uphold that trust and be genuinely responsible with the data you collect.
Data Privacy Laws
There are a number of privacy regulations around the world pushing for better protection of personal information and emphasizing data privacy.
Europe’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is leading the charge, saying consumers must have control over their own data and companies must be clear about how they use it.
In the U.S., the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) reinforces this idea, demanding businesses be upfront about their data practices.
Over in Canada, the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) outlines that companies can’t just take someone’s personal information – they need to obtain permission first.
Data Privacy Best Practices
Knowing the essential components of data privacy and how to implement them will help you address privacy concerns better and handle sensitive data properly. Let’s take a look at some of the best practices for data privacy:
- Consent: It’s simple. Before collecting or using someone’s data, get a clear go-ahead from the user. And this shouldn’t be buried in jargon; it should be as clear as day.
- Transparency: Users deserve clarity. If you’re collecting data, let them know why and how. Transparent practices aren’t just a nice-to-have — they’re a cornerstone of trust-building.
- Data Minimization: Don’t collect data for the sake of collecting. Only gather what’s necessary. In other words – if you don’t need it, don’t store it.
- Access and Correction: People should easily see their own data and fix any errors. It’s about giving users control over their own information.
- User Rights: Beyond just accessing data, users have rights. Whether it’s the right to be forgotten or portability rights, you need to explain them in your privacy policy and uphold them.
- Data Sharing and Third Parties: If you’re sharing data with third parties, be open about it. Users should know who has their data and for what purpose.
- Compliance with Regulations: Various regions have their data privacy requirements to help protect sensitive information. Whether it’s GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California, compliance isn’t optional.
ALSO READ: Download the Privacy Policy Template for Your Website
What Is Data Security?
Data security is the practice of protecting digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, or theft to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data. It’s a critical aspect of maintaining user trust and complying with security and privacy regulations.
It’s a term that likely resonates with many online business owners. Think of all the sensitive data you handle: customer information, financial records, proprietary content, and more.
Without adequate security measures in place, this data is vulnerable. Not only could a breach harm your customers, but it could also severely damage your brand’s reputation and lead to financial losses.
Data Security Best Practices
Implementing robust data security means deploying a combination of strategies. Some of the best data security practices to protect sensitive data from malicious use include:
- Encryption: Encryption is the conversion of data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. Think of it as scrambling your data so only someone with the right “key” can unscramble it.
- Access Controls: This is about defining who can access what data and when. By setting strict controls, you ensure that only authorized personnel can view or modify sensitive information.
- Regular Audits: Conducting audits lets you review system activities, ensuring that access and data modification remain in compliance with set policies.
- Backup Solutions: Backing up data means having a secondary copy stored securely. If the primary data is compromised or lost, you can restore it from the backup.
- Two-factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA requires a second form of identification beyond a password. This might be a texted code or a fingerprint.
- Regular Updates: Software and systems need regular updates to patch vulnerabilities. Updating your systems helps fend off new threats and keep your systems secure.
- Incident Response Plan: Have a plan ready for when a data breach or security incident occurs. This ensures a fast and efficient response, minimizing potential damage.
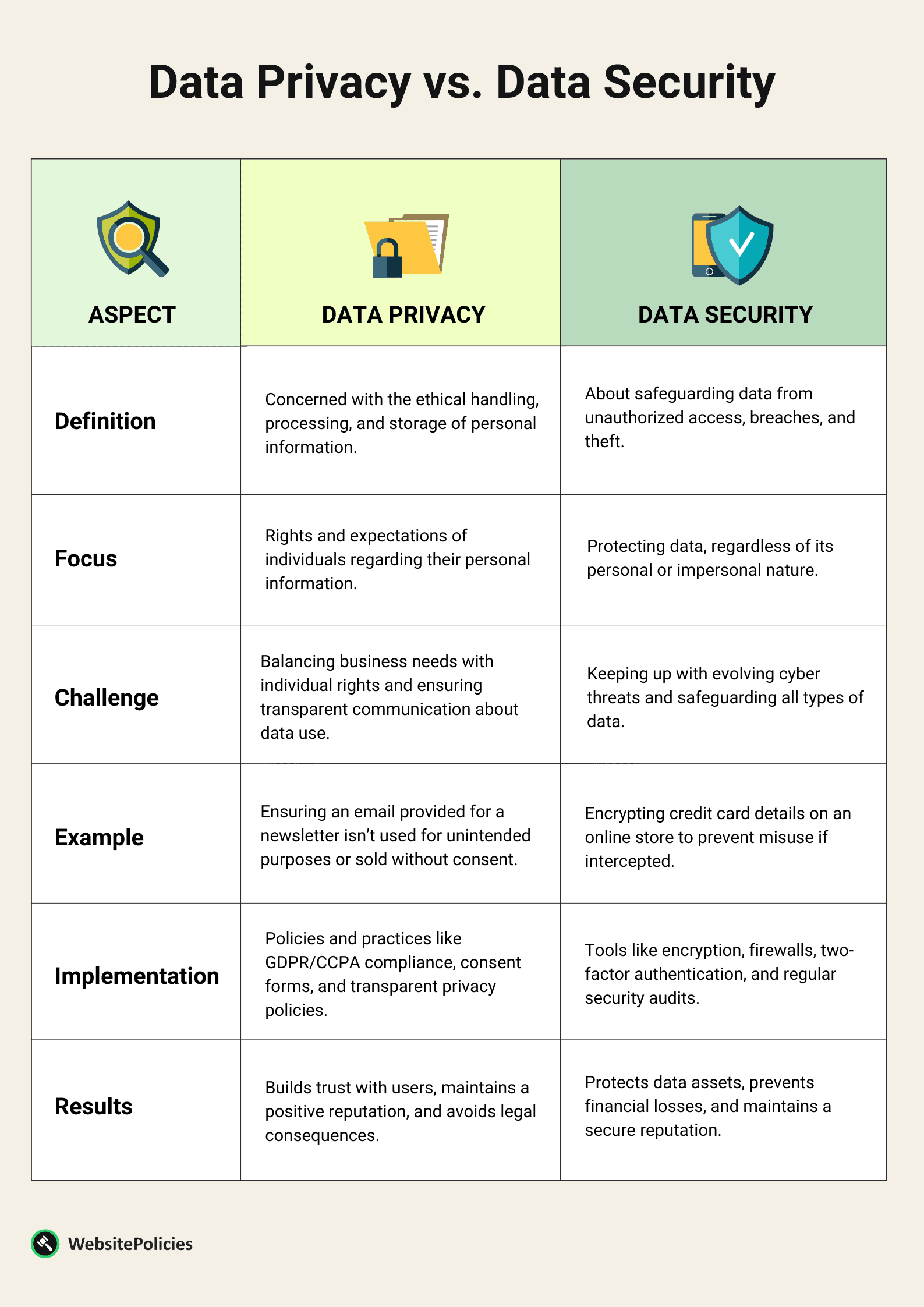
Data Privacy vs Data Security: Key Differences
While both data security and data privacy have their distinct concerns, they’re complementary and are meant to help you protect data. One ensures the right use of data, and the other makes sure it’s shielded from threats. It’s essential to prioritize both.
Below is a list of differences between data privacy and data security with some examples to make it even easier to understand:
How Does Data Security Affect Data Privacy?
Data privacy and security, while distinct concepts, are intertwined. Think of data security as the protective measures you implement to guard your data from unauthorized access or breaches.
This includes using encryption, firewalls, and other technical solutions to keep malicious actors at bay. When your security is robust, the data you collect remains in your control and out of the hands of cybercriminals.
On the other hand, data privacy focuses on ensuring that personal information is handled, shared, and stored in ways that respect the rights of individuals.
If your security measures fail, the privacy of the individuals whose data you possess is at risk. A security breach can lead to unauthorized access, misuse of personal data, or even its sale on the dark web.
So, in essence, while data security zeroes in on safeguarding data from threats, data privacy is about how this data is used and shared.
PRO TIP: By maintaining strong security measures, you inherently protect the privacy of the data you hold.
Can You Have Data Security Without Privacy?
Even if your data is secure, it doesn’t necessarily mean it’s private.
Data security is about protecting personal data from unauthorized access or theft. It’s like locking your front door to prevent burglars from entering.
When you implement strong security measures like encryption and firewalls, you’re essentially putting up barriers to ensure your data stays safe.
Data privacy on the other hand is about ensuring that the data, even if accessed, is used in a respectful manner and only for its intended purpose.
Imagine if someone had a key to your front door, they might not break anything or steal, but they’d still see all the intimate details of your life.
It usually helps and is actually required by law, to have a valid privacy policy on your website that explains your data collection and handling practices. So don’t forget to have one readily available.
To sum up, while you can have security without privacy, it’s not ideal. If you only focus on security, you might overlook how data is being shared or used.
As a data holder, it’s your responsibility to ensure both robust security and unwavering privacy to truly safeguard your users and their trust.
Frequently Aske Questions
What’s the difference between data privacy and data security?
Data privacy concerns the ethical handling and usage of personal information, ensuring it’s used as intended. Data security focuses on protecting this data from unauthorized breaches and theft.
Are there laws that mandate data privacy and security?
Yes. Laws such as Europe’s GDPR, the U.S.’s CCPA, Canada’s PIPEDA, and others emphasize user control over data and clear communication from businesses on data usage.
What are common data privacy measures?
Privacy measures include obtaining explicit user consent, providing clear privacy policies, ensuring transparency in data collection and use, data minimization practices, and more.
What are common data security measures?
Common measures include encryption, access controls, regular audits, backup solutions, two-factor authentication, regular software updates, and having an incident response plan.
What are some best practices for data privacy?
Key practices include obtaining clear user consent, being transparent about data usage, minimizing unnecessary data collection, and respecting user rights like data correction.
Can you ensure data security without ensuring privacy?
While you can technically secure data from breaches, it doesn’t ensure that the data is used ethically. Both security and privacy are essential for user trust.



